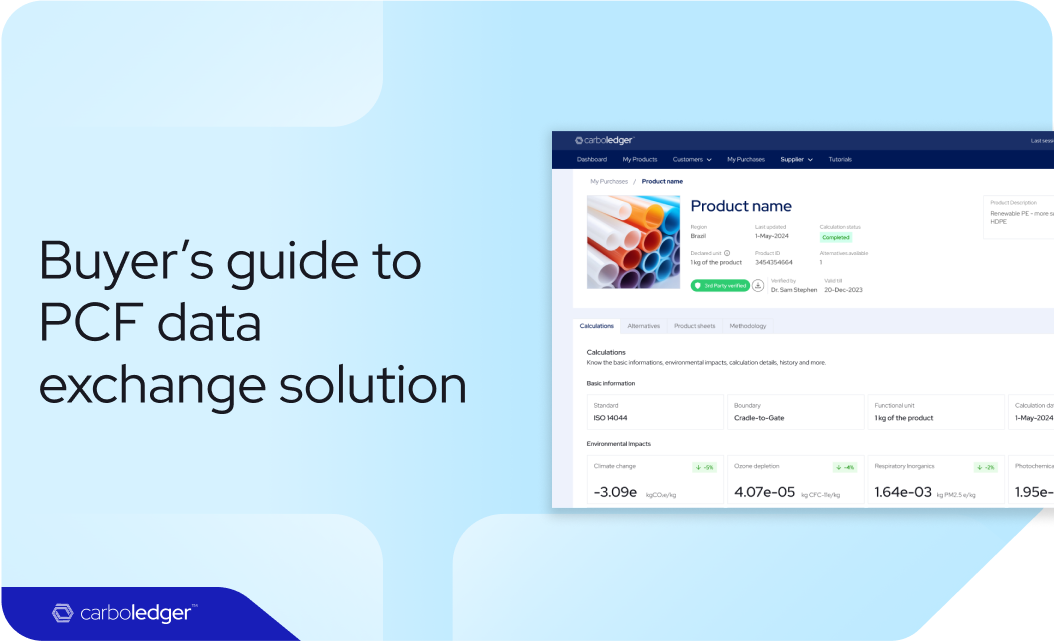
Presenting or communicating the results of any complex process necessitates planning out how it needs to be communicated. This requires examining the key aspects of communication mentioned below:
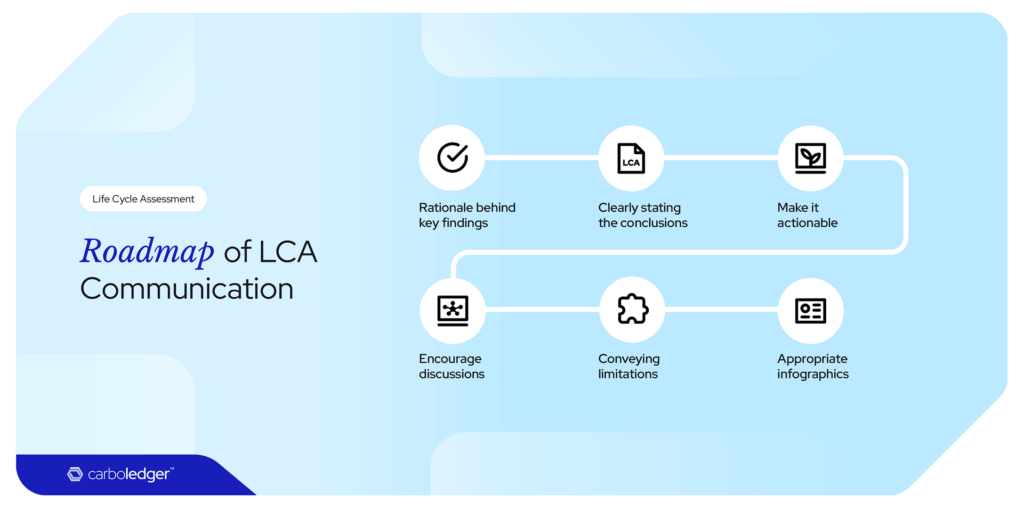
Rationale behind key findings
Life cycle assessments carry meaning when system boundaries, data sources, and assumptions are stated clearly. It is important to discuss any uncertainties or limitations in the data or methodology. Provide context for the findings by comparing them to industry benchmarks or previous studies.
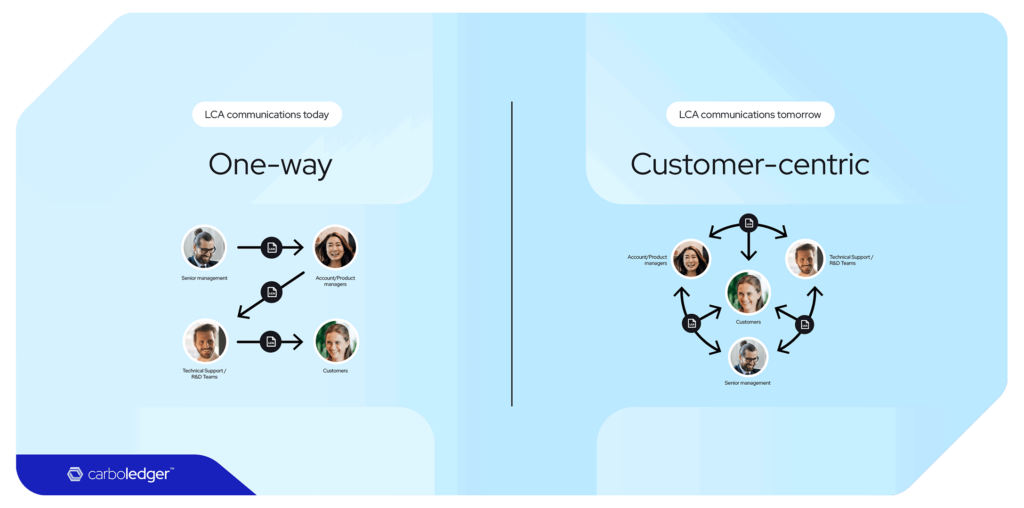
Depending on the audience, the rationale may vary, and it is important to adapt your communication to the audience. For example, the customer will find it valuable to understand the data sources and system boundaries in order to evaluate how they can utilise this data. For internal stakeholders, the actual results and hotspots will be more valuable since it can help them take action in the right direction
Clearly stating the conclusions
Summarize the main takeaways from the LCA in a concise and impactful way. Try to avoid technical jargon and use clear, actionable language. Quantify the environmental benefits wherever possible during communication.
For external customers, the conclusions can be presented in ISO, TfS, or WBCSD formats to make the data useful for them. For internal stakeholders, it will be valuable to use internal process information and leverage your company culture to state the conclusions. This will help the audience feel connected to you and the outcomes of the results and you can
Make it actionable
Suggest specific actions that can be taken to improve the environmental performance of the product or service. Prioritize the recommendations based on their potential impact and feasibility. Offer resources and support to help stakeholders implement the recommendations.
Prioritize recommendations based on impact and feasibility. For example, for carbon footprint reduction, exploring renewable energy sources for production can be a feasible recommendation. Remember to incorporate feedback and collaboration from interested departments during this time to make it actionable.
Encourage discussions
It is important to encourage dialogue for effective LCA communication. Invite questions, feedback, and discussion with stakeholders. Open communication fosters deeper understanding and collaborative action towards informed decision-making and sustainable product development.
Organizing an interactive session or open forum can facilitate dialogue and understanding, as well as encourage everyone to ask questions and share their thoughts on the LCA findings.
Conveying limitations
Explain the limitations that came up when the assessment was conducted. It is important to convey that LCA cannot predict the actual impacts and should never be used as the sole basis for comparative assertions.
Let the audience know that LCA is based on assumptions and estimations, and actual environmental impacts might vary. Clarify that this study provides valuable insights, acting as a starting point for continuous improvement
Appropriate infographics
Visualizing the data using infographics provides a better understanding of the data for those who are involved and makes it available to those who are not involved. Data visualization empowers stakeholders to compare diverse impact categories across different units, leading to informed decision-making.
The infographics can be tailored according to the audience’s needs. For a customer, it can be a clear bar chart comparing the product’s impact across different categories with industry benchmarks. For an internal stakeholder, it can be a detailed heat map visualizing the life cycle stages and highlighting the “hotspots” for various environmental indicators.